Unveiling the Distinction: Ester and Ether in Thermoplastic Polyurethane Resin
Thermoplastic Polyurethane Resin (TPU) is a versatile material widely used in various industries due to its exceptional properties. Understanding the components that make up TPU is crucial in comprehending its characteristics. In this blog post, we will explore the difference between esters and ethers and their roles within the framework of TPU, shedding light on their influence on the properties and applications of this remarkable resin.
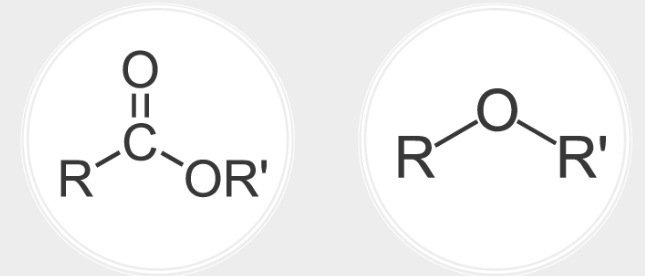
Esters are essential components in the production of TPU. They are formed by the reaction of diisocyanates with polyester diols. Esters contribute to the flexibility and durability of TPU, allowing it to exhibit excellent mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elongation. The ester groups in TPU also offer resistance to oils, chemicals, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including footwear, automotive parts, tubing and extruded shapes, and caster wheels.
Ethers, on the other hand, play a crucial role in imparting resilience and elasticity to TPU. They are obtained by reacting diisocyanates with polyether diols. The presence of ether linkages in TPU enhances its hydrolysis and UV resistance. Additionally, ethers contribute to TPU's resistance to low temperatures and microbial growth. They also provide a lower density material than ester based options. These characteristics make ether based TPU suitable for applications such as golf discs, cattle tags, sports equipment, and outdoor tools
The distinction between esters and ethers within Thermoplastic Polyurethane Resin highlights their respective contributions to the properties and applications of this versatile material. Esters provide TPU with durability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, while ethers enhance its weatherability and low temperature performance. Understanding the role of esters and ethers in TPU empowers engineers and designers to harness the full potential of this remarkable resin in diverse industries.